Distribution of dividends to shareholders can be in the form of cash or stock. Cash dividends represent a cash outflow and are recorded as reductions in the cash account. These reduce the size of a company’s balance sheet and asset value as the company no longer owns part of its liquid assets. Retained earnings, also known as earned surplus or accumulated earnings, are a measure of a company’s cumulative net profits after subtracting dividends paid to shareholders. It represents the amount retained earnings on balance sheet of profit that a company has retained and reinvested back into the business since its inception.
- When it comes to assessing the state of a company’s finances, retained profits and revenue are both significant factors; nevertheless, they both shed light on something different about the overall financial picture.
- To calculate beginning retained earnings, take the previous year’s ending retained earnings balance.
- For investors and financial analysts, retained earnings are essential since they offer in-depth insights into a company’s long-term growth potential.
- This is because the company doesn’t use that item, or records them differently.
- The income statement shows the performance of the business throughout each period, displaying sales revenue at the very top.
- Even with context, this figure will only show how much money is added or taken from retained earnings.
Provide a heading
Companies that are profitable are able to create value efficiently because they are able to use their retained earnings to fund initiatives. Bookkeeping vs. Accounting Be advised that the value creation computation provided above is limited to the usage of retained earnings and does not reflect the company’s total value creation. In order to better grasp what retained earnings can reveal, the following possibilities cover all of the potential uses of an organization’s excess funds. In the first case, for example, the company’s earned money would permanently disappear from the accounts and books due to the irreversible nature of dividend payments. Samsung Inc. earned a net profit of 500,000 during the accounting period Jan-Dec 20×1. The company decided to retain the profits for that year and invest the retained earnings in expanding the business.
minutes to understand retained earnings and how to account for them
With this online accounting software, you can easily track and manage the growth of retained earnings, helping your business make informed financial decisions and maintain a clear picture of its financial health. This holistic approach allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of a company’s potential for long-term success. Retained earnings on the balance sheet are a critical component of a company’s financial health and performance. They represent the cumulative profits that have been retained and reinvested in the business, showcasing the company’s ability to generate profits and its commitment to long-term sustainability. Analyze the balance sheet’s retained earnings along with other financial statements to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health, profitability, and strategic focus.
Another example of retained earnings calculation
Retained earnings are calculated by taking the beginning-period retained earnings, adding the net income (or loss), and subtracting dividend payouts. In conclusion, retained earnings on the balance sheet provide a glimpse into a company’s financial journey, profitability, and reinvestment efforts. It serves as a valuable tool for investors, analysts, and stakeholders to assess a company’s financial health, growth potential, and commitment to creating sustainable shareholder value.
Once dividends have been paid out, a company’s net profits or earnings are known as retained earnings. An essential idea in accounting, “retained” conveys the idea that the corporation kept those earnings rather than paying dividends to shareholders. To build a reliable forecast, begin with a starting retained earnings balance from your most recent financial close. Next, model revenue growth drivers such as new product launches or market expansion, and estimate corresponding profit margins after accounting for operating expenses and taxes.

This continuity emphasizes the cumulative nature of retained earnings and their role in the company’s overall financial position. Retained earnings are crucial for a company’s growth and long-term sustainability. By reinvesting profits into the business, companies can finance expansion initiatives, research and development, debt repayment, or acquisitions. Retained earnings also serve as a cushion during challenging times, helping companies withstand economic downturns or financial setbacks. A high level of retained earnings may be a sign of solid financial health, as it shows that the company has been profitable in the past.
- In fact, after ten years, a CEO could be responsible for managing more than 60% of a company’s capital simply through decisions related to retained earnings.
- The last entry on the statement is the final amount after dividends have been deducted.
- First, you have to figure out the fair market value (FMV) of the shares you’re distributing.
- Retained earnings are the profits that a company has earned to date, less any dividends or other distributions paid to investors.
- This money can be used to fund business expansions or to finance new projects and product development, propelling the company’s growth.
- When a company consistently retains part of its earnings and demonstrates a history of profitability, it’s a good indicator of financial health and growth potential.
If your business currently pays shareholder dividends, you’ll need to subtract the total paid from your previous retained earnings balance. If you don’t pay dividends, you can ignore this part and substitute $0 for this portion of the retained earnings formula. The main difference between retained earnings and profits is that retained earnings subtract dividend payments from a company’s profit, whereas profits do not. Where profits may indicate that a company has a positive net income, retained earnings may show that a company has a net loss, depending on the amount of dividends it paid out to shareholders. Both revenue and retained earnings are important in evaluating a company’s financial health, but they highlight different aspects of the financial picture. Revenue sits at the top of the income statement and is often referred to as the top-line number when describing a company’s financial performance.
On the other hand, when a company generates surplus income, a portion of the long-term shareholders may expect some regular income in the form of dividends as a reward for putting their money into the company. Traders who look for short-term gains may also prefer dividend payments that offer instant gains. However, it’s crucial to note that interpreting retained earnings solely based fixed assets on numeric figures can be misleading. It’s essential to consider the company’s overall business strategy, market positioning, management’s decision-making, and industry-specific dynamics to gain a holistic understanding of retained earnings. When a company retains its earnings, it essentially preserves a portion of its profits for reinvestment.
How Are Revenue and Retained Earnings Different?

The cash flow statement then takes net income and adjusts it for any non-cash expenses. Then cash inflows and outflows are calculated using changes in the balance sheet. The cash flow statement displays the change in cash per period, as well as the beginning and ending balance of cash. They earn $50,000 in net income and decide to reinvest $30,000 into new materials and expansion, while still paying $20,000 in dividends. This reinvestment fuels their growth, showing how retained earnings are the unsung heroes that help entrepreneurs expand and brave economic storms without begging for outside cash. The statement of retained earnings is a key financial report showing how much profit a company reinvests.
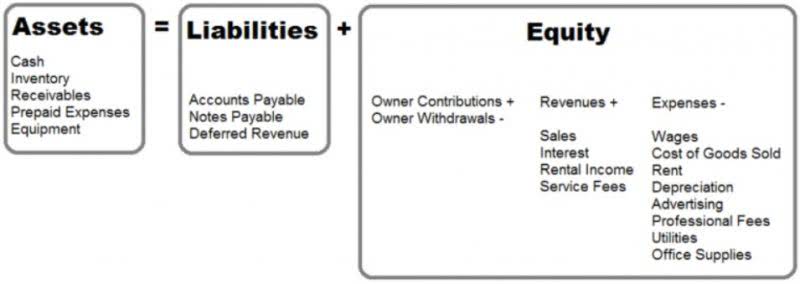
How Are Profits and Retained Earnings Related?
- This technique provides a reliable backstop when traditional data sources fall short and helps validate the equity section holistically.
- 73% of CFOs feel pressure to adopt investments in AI—but what else is top of mind for finance leaders?
- The formula to calculate retained earnings starts by adding the prior period’s balance to the current period’s net income minus dividends.
- Retained earnings and profits are related concepts, but they’re not exactly the same.
- They often rely on dividends as a primary source of income from their investments.
- It’s the number that indicates how much capital you can reinvest in growing your business.
Retained earnings show a credit balance and are recorded on the balance sheet of the company. Before you can include the net income in your statement of retained earnings, you need to prepare an income statement. Unappropriated retained earnings have not been earmarked for anything in particular. They are generally available for distribution as dividends or reinvestment in the business. Retained earnings are the cumulative profit a company keeps within the business vs. distributing to owners, shareholders, or other stakeholders. To better understand how to find retained earnings, let’s consider two examples.